If you want to find a natural treatment for your PCOS, don’t pass by berberine. PCOS causes many symptoms from several root causes, such as high androgens, insulin resistance, inflammation, weight gain, and more. And unfortunately, many of these contribute to the other in a vicious cycle.
Today, we’ll look at the science behind berberine supplements for treating common symptoms of PCOS. These sources come from peer-reviewed journals published in the National Library of Medicine. Let’s learn more about this promising plant-based supplement.
What Is Berberine?

Branch with Red Barberries
Berberine is a natural plant chemical from the genus Berberis. It comes from the leaves, roots, and bark of plants such as European barberry, Phellodendron, goldthread, Oregon grape, and tree turmeric. It can have a yellow color and bitter taste. This natural supplement has been used in traditional medicine methods in many countries, including Nepal, Iran, India, and China.
To understand the functions of berberine, we need to understand a few processes that impact PCOS.
What Are Androgens?
Androgens, known as male sex hormones, occur in women, just in lower amounts. They contribute to hundreds of processes in the female body, including puberty, sexual function, reproduction, bone growth, and organ function. The adrenal glands, ovaries, and fat cells produce androgens.
These hormones also play an essential role in converting androgens to estrogens, the female hormones. Some of the main androgens include testosterone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione.
But when these levels are too high, it can contribute to polycystic ovarian syndrome and other symptoms such as male-patterned hair growth, especially on the face, hair loss on the head, acne, menstrual irregularities, infertility, blood sugar abnormalities, and more.
To treat these symptoms, you need to lower the amount of androgens in the body. Keep reading to learn how berberine may help.
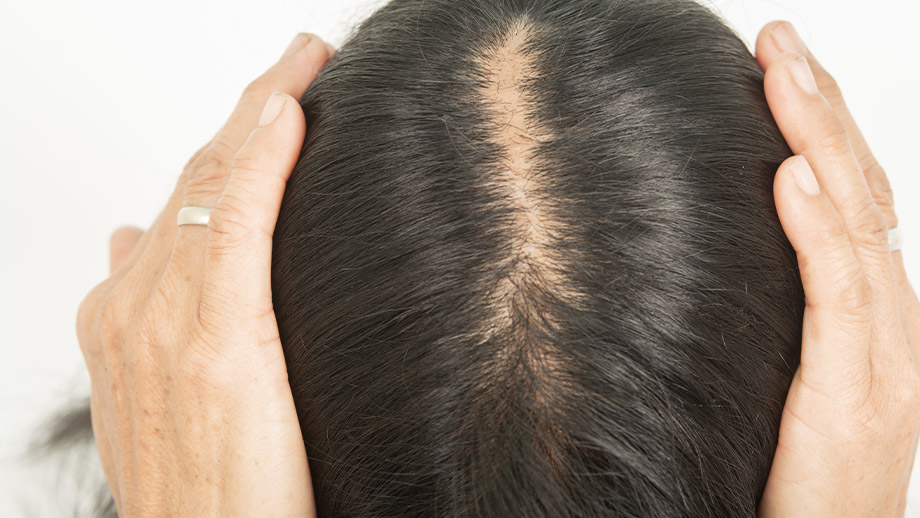
Hair Loss In PCOS – Caused By High Androgens
What Are the Evidence-Based Benefits of Berberine for PCOS?
The emerging studies on the benefits of berberine for treating PCOS have found consistent results. These include improvements to weight loss, insulin resistance, cholesterol, and fertility. Many of these studies also compared it to other treatments such as metformin, letrozole, and myo-inositol.
So, let’s dig into what berberine can do and why it might be an effective option for treating symptoms of your PCOS.
Lowers Androgens
High androgen levels cause many symptoms of PCOS. Berberine can help lower these levels. One study comparing berberine to myoinositol and metformin found “the decrease in free androgen index in the group receiving berberine was significantly more than the group receiving myoinositol.”
With lower androgens, you can expect improvements in acne, hair loss, and hair growth, among many other symptoms associated with PCOS.
The study further stated that “Berberine significantly increased levels of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) compared to metformin and myo-inositol.”
SHBG helps regulate the use and transport of androgens and estrogens to specific tissues. Having more SHBG helps your body properly use the androgens and decreases the symptoms associated with them.
Improves Weight Loss
Several studies confirmed the use of berberine for weight loss. The study on the effects of berberine stated it had better outcomes on waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio than myo-inositol and metformin groups. But you can take berberine with myo-inositol and metformin as well.
Another study on berberine for PCOS management says “that berberine induced a redistribution of adipose tissue, reducing visceral fat mass even in the absence of weight loss.” This implies it can have beneficial effects on improving PCOS belly.
Research on the efficacy and safety of berberine showed “that berberine can inhibit fat-forming and lipogenic genes of fat, thereby reducing fat production.” It also accelerated the glucose and fat metabolism.
According to the research, it reduces fat production and body-fat ratio, improves insulin sensitivity, and promotes glucose transport. It also helps sugar and fat decompose instead of accumulate.
Furthermore, berberine’s weight loss and anti-inflammatory components may play a role in improving the symptoms of metabolic disorders.
These promising results were backed by at least three studies on women with PCOS and a systematic review and meta-analysis of five randomized clinical trials.

Berberine May Improve Weight Loss
Reduces Insulin Resistance
A key component of PCOS relates to insulin resistance. This means the cells resist insulin, which shuttles glucose into the cell. If the cell can’t get enough glucose, it won’t have the energy to perform its duties.
According to the research, berberine, metformin, and myo-inositol all improved fasting insulin levels. However, myo-inositol had a better ratio of fasting blood glucose and serum fasting insulin levels than the other two.
However, the study on its efficacy and safety found that “berberine-mediated AMPK activation has an anti-inflammatory effect, which improves insulin resistance.”
So, while myo-inositol may produce a better glucose and insulin ratio, berberine also significantly reduces insulin resistance and helps balance blood sugar levels. However, metformin, myo-inositol, and berberine have all improved insulin resistance and can work as effective treatments for PCOS, according to available research studies.
Lowers Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Risks
While cholesterol itself is not a primary characteristic of PCOS, there can be a connection between PCOS and certain lipid abnormalities, including cholesterol imbalances.
Additionally, insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances in PCOS can lead to lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, known as “good” cholesterol, and higher levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol. These levels are also associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
Research suggests that berberine could have a positive effect on cholesterol levels, including reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and total cholesterol levels.
Berberine’s potential to regulate cholesterol could offer several benefits for women with PCOS, who might be at an increased risk of lipid abnormalities.
Several studies found that this supplement improved total cholesterol, serum triglyceride, serum LDL, and increased serum HDL. Thus, it improves good cholesterol, lowers bad cholesterol, and improves triglycerides. Compared to metformin and myo-inositol, “berberine supplementation improved the lipid profile parameter the most.”
Additionally, berberine’s anti-inflammatory properties might help mitigate the chronic low-grade inflammation seen in PCOS, which can positively impact cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
Improves Fertility

Berberine May Improve Fertility
Women with PCOS can experience infertility due to hormonal imbalances, lack of ovulation, and poor ovarian function.
Berberine may influence hormone levels critical for ovulation, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). By promoting a healthier hormonal balance, berberine might increase the likelihood of regular ovulation.
Additionally, some preliminary studies suggest that berberine might positively impact egg quality, potentially leading to higher chances of successful conception.
Due to berberine’s effects on insulin and androgen function, it can lead to improvements in ovulation, menstruation regularity, and implantation.
In another study, it improved the insulin resistance of theca cells associated with ovarian follicles. Thus, it enhances ovulation rates per cycle and live birth rates. Though many functions aren’t fully understood, this supplementation has also led to improved IVF outcomes.
Berberine Vs Metformin: Which Is Better?
Many of the studies referenced above compare berberine and metformin for treating PCOS. They found that in some cases berberine provided better results, while other studies found they had equal results. Now while they both improve insulin resistance, androgens, lipid profile, and ovulation, they aren’t exactly equal.
Metformin is a perscription medication for PCOS that works by reducing liver glucose production and increasing insulin sensitivity. It helps lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin function, which can benefit women with PCOS who have insulin resistance.
However, metformin can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. And some individuals may experience vitamin B12 deficiency with long-term use. Berberine on the other hand has few side effects and a lower risk of vitamin deficiency.
Furthermore, berberine is a natural compound available as a dietary supplement. You can purchase it without a prescription in many countries, although you should still consult your doctor about using it. But metformin should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
The effectiveness of both berberine and metformin can vary from person to person. Some women may respond better to one treatment than the other. Additionally, factors such as genetics, overall health, and the specific manifestations of PCOS may influence which one you choose.
Ultimately, you must consult with a healthcare provider who can evaluate your specific PCOS profile and help you determine the most appropriate treatment approach for your needs.
Always remember that PCOS management is highly individualized, and what works best for one person may not be the same for another. So which is better? Only you can decide that.

Metformin: Is It Right For You?
When Is the Best Time to Take Berberine?
You can take berberine anytime, but to avoid any potential stomach upset, you can take it before a meal. This can also help manage blood sugar spikes when eating. Additionally, taking it before you eat can ensure better absorption without interference from your food.
Is Berberine Safe?
A study on the efficacy of berberine says that using it for more than three months improves treatment outcomes. However, research doesn’t say whether you can safely take it for more than six months to a year.
Thus, we suggest taking a one-month break every six months. Additionally, you need to stop taking berberine when pregnant and breastfeeding.
Furthermore, berberine can interfere with certain prescriptions, such as blood pressure and diabetes medications. You can take berberine with metformin if taken at the same time. However, taking berberine a couple of hours before metformin may increase the amount of metformin in the body, which can make your blood sugar drop too low.
Always ask your doctor about any supplements you take, especially when on other medications.
Are There Any Berberine Supplement Side Effects?
Berberine is considered a safe and effective natural supplement. Most studies report few to no adverse effects.
One study stated, “the adverse effects reported are mild, transient, and sporadic: anorexia/loss of appetite, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and flatulence.”
However, out of these studies, only one out of 214 participants reported gastrointestinal side effects. You also want to ensure you don’t have any allergies to berberine before using it.
What’s the Optimal Berberine Dosage for PCOS?
According to a study, “the dosage of [Berberine] used to treat different metabolic diseases ranges from 0.4 g/day to 1.5 g/day.” Most supplement brands will contain between 500 milligrams to 1 gram per serving.
You can ask your doctor what they would recommend. They may advise taking the smaller dosage first to avoid gastrointestinal effects.
Where to Buy Berberine Supplements?
You can find berberine supplements in health food, vitamin, and drug stores. However, as it is not a common supplement, you may have trouble finding it in certain areas.
Be careful when buying online, especially from places like Amazon or unknown websites. You never know what you’ll get from sketchy companies. Always check reviews and verify the company and source.
However, you can also purchase berberine from the Health & Balance Vitamins online store. These capsules contain 500 milligrams of berberine and ginger root extract. You can buy them in a pack of 30, 60, or 180 capsules and take them once a day. You can also subscribe and save, so you don’t have to worry about running out. They’ll arrive straight to your door.
So, Is Berberine for PCOS Worth It?
It’s worth noting that berberine’s potential benefits for androgen regulation, insulin sensitivity, weight management, hormonal balance, and cholesterol levels can work together synergistically to improve overall health in women with PCOS. By addressing these interconnected factors, berberine might offer a holistic approach to managing both PCOS symptoms and associated cardiovascular risks.It also has fewer side effects than comparable medications such as metformin. The research is clear: berberine has many significant benefits for women with PCOS.
As with any supplement or intervention, consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating berberine into your routine, especially if you have PCOS or any existing medical conditions. They can help assess whether berberine is appropriate for your situation, consider potential interactions, and provide guidance on the proper dosage.
Do you think berberine is worth it? Let us know below.












